Introduction
Starting the journey to become a certified trauma therapist isn’t just about choosing a career; it’s a heartfelt commitment to healing and supporting individuals who have faced unimaginable challenges. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and requirements for achieving certification, from understanding educational prerequisites to navigating the application process.
As you embark on this meaningful path, you might find yourself asking:
- What specific qualifications do I need?
- How can I ensure I’m truly prepared to make a difference in my clients’ lives?
Exploring these questions can illuminate the way forward for those ready to embrace this vital role in mental health care.
Understand Certification Requirements
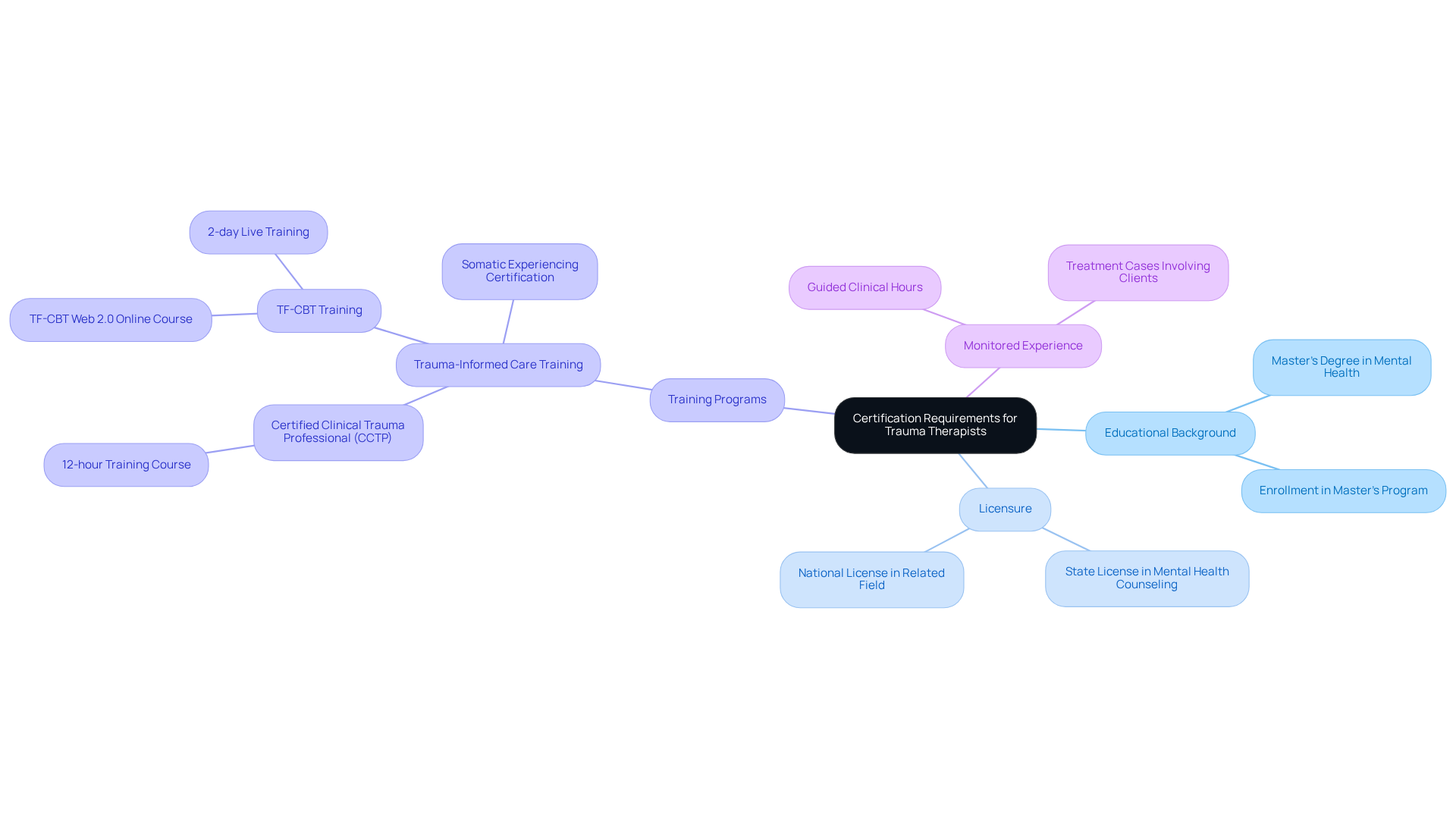
To become a certified trauma therapist, understanding the accreditation requirements set by various certifying organizations is essential. Let’s explore what you need to embark on this meaningful journey:
- Educational Background: Most qualifications ask for at least a master’s degree in a mental health-related field, like psychology, social work, or counseling. If you’re currently enrolled in a master’s program, some qualifications may still welcome you.
- Licensure: Holding a state or national license in mental health counseling or a related field is crucial. This ensures you’re legally permitted to practice and provide therapy, giving you the confidence to support others.
- Many qualifications also require you to complete specific training programs focused on trauma-informed care. For instance, the Certified Clinical Trauma Professional (CCTP) credential involves finishing a 12-hour training course, equipping you with essential skills.
- Monitored Experience: Some credentials may require a certain number of guided clinical hours working with clients facing distress. This hands-on experience is vital for developing practical skills and deepening your understanding of their needs.
By ensuring you meet these requirements, you can confidently take the next steps toward becoming a certified trauma therapist for emotional distress. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? If so, know that seeking help is a courageous step toward healing. Your journey to becoming a compassionate therapist can truly make a difference in the lives of those who need support.
Explore Different Trauma Certification Types
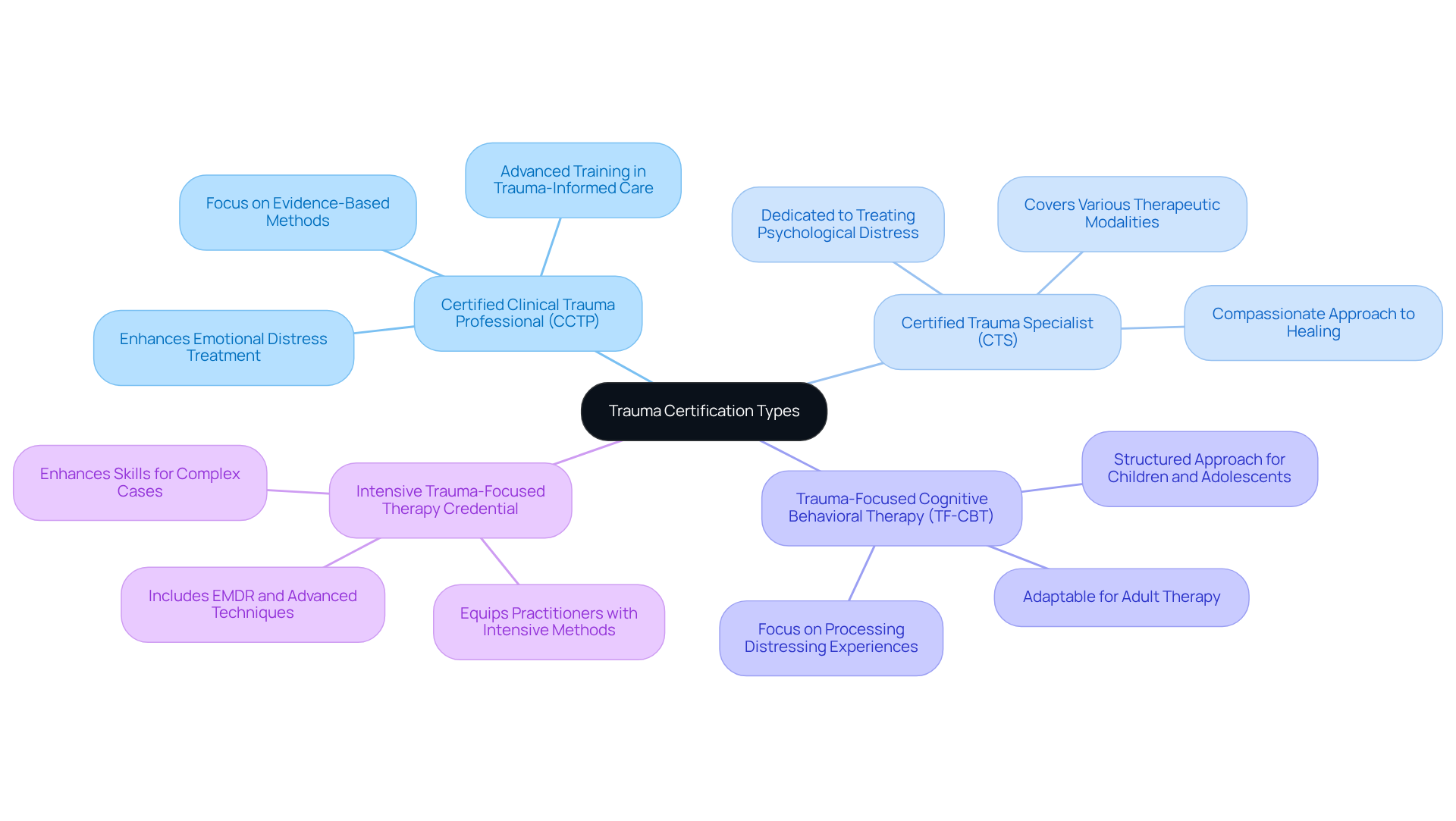
When it comes to trauma therapy, various qualifications, such as those of a certified trauma therapist, cater to different aspects of injury treatment, each offering unique benefits. Let’s explore some of the most recognized certifications that can guide you on your healing journey:
-
Certified Clinical Trauma Professional (CCTP): This credential offers advanced training in trauma-informed care, making it a wonderful choice for licensed mental health professionals. It emphasizes evidence-based methods and therapeutic strategies that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of emotional distress treatment.
-
Certified Trauma Specialist (CTS): Designed for those dedicated to treating psychological distress, this certification covers a range of therapeutic modalities and techniques aimed at helping individuals navigate their experiences with compassion and understanding.
-
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): Tailored for professionals working with children and adolescents, this qualification focuses on a structured approach to support younger clients in processing distressing experiences. While it primarily serves younger populations, the principles of TF-CBT can also be adapted for adult therapy, making it versatile.
-
Intensive Trauma-Focused Therapy Credential: This credential equips practitioners with intensive methods for addressing psychological distress, including EMDR and other advanced techniques, enhancing their skills for managing complex cases.
As you consider these options, think about which credential resonates with your professional goals and the specific needs of those you wish to help. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Exploring these qualifications can be a step toward finding the right path for healing, both for yourself and as a certified trauma therapist for your future clients.
Navigate the Application Process
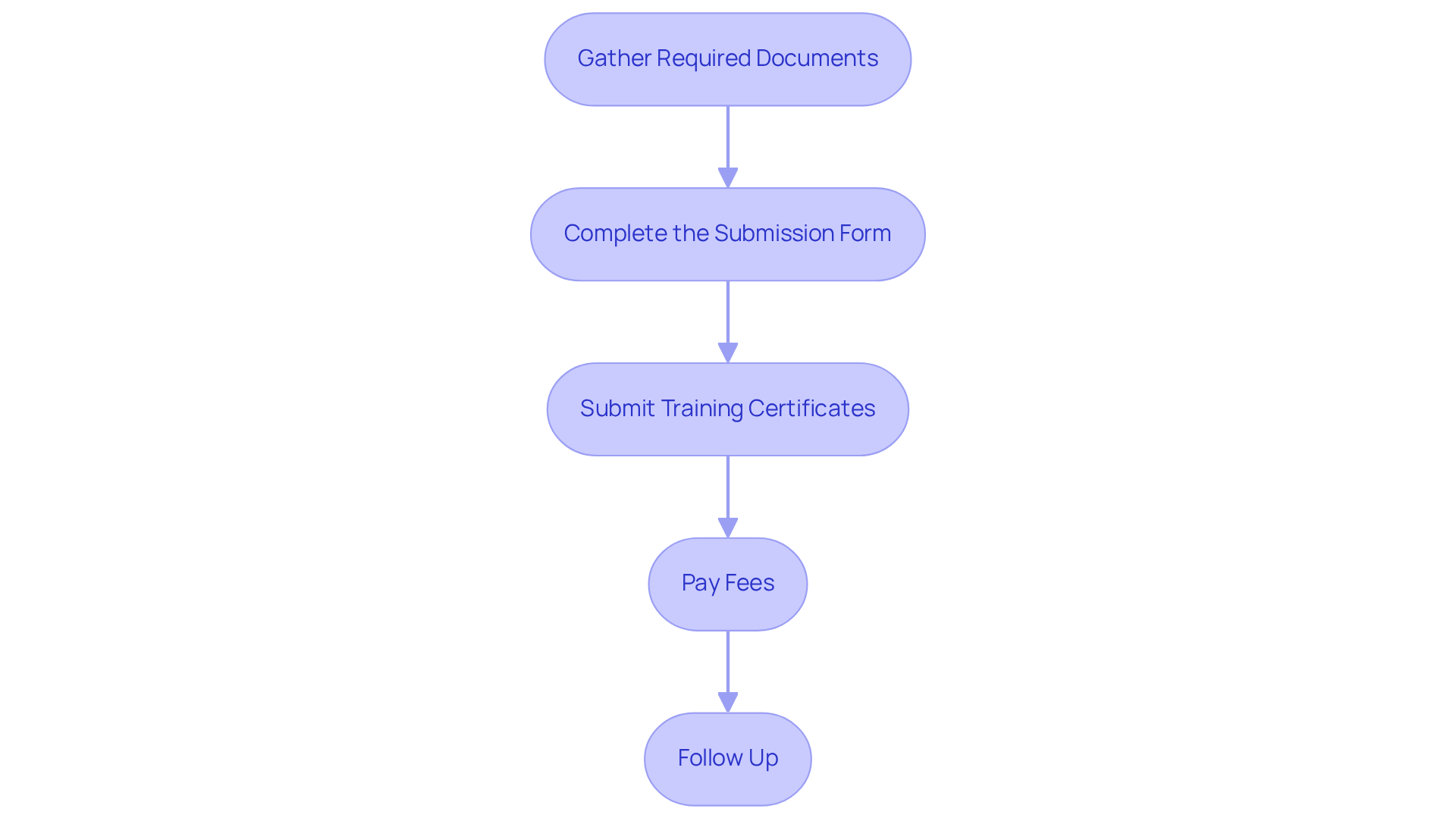
Navigating the application process for trauma therapist certification can feel overwhelming, but with these essential steps, you can approach it with confidence and clarity:
- Gather Required Documents: Start by preparing your educational qualifications, including transcripts and diplomas, along with proof of licensure. Having these documents organized will not only simplify your process but also ease your mind.
- Complete the Submission Form: Take your time filling out the submission form from the certifying body. Accuracy is crucial here; double-check your responses to prevent any delays in processing. Remember, this is a step towards your goal.
- Submit Training Certificates: If your credential requires specific training, be sure to include copies of your completion certificates. For instance, applicants for the CCTP must provide proof of completing the required 12-hour training. This shows your commitment to your professional development.
- Pay Fees: Most certifications require a processing fee. Confirm the accepted payment methods and ensure your payment is included with your submission. This is a small investment in your future.
- Follow Up: After submission, reach out to the certifying body to confirm receipt of your application and inquire about the expected processing timeline, which typically takes about 45 days. This proactive step can help ease any anxiety you may have.
Additionally, keep in mind that the credential is valid for three years, and certified members must complete 30 hours of trauma-related continuing education for recertifying. It’s also essential to adhere to Evergreen Certifications’ Professional Code of Ethics when applying for credentials.
By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth application process, bringing you closer to your goal of becoming a certified trauma therapist. Remember, this journey is not just about meeting requirements; it’s a chance to reflect on your dedication to helping survivors in their healing processes. Have you ever felt the call to support others in their most vulnerable moments? This is your opportunity to make a meaningful impact.
Maintain Certification Through Continuing Education
To uphold your credential as a crisis therapist, participating in continuing education (CE) is vital. Have you ever felt the weight of responsibility in your role? Here’s how to ensure you meet these important requirements:
-
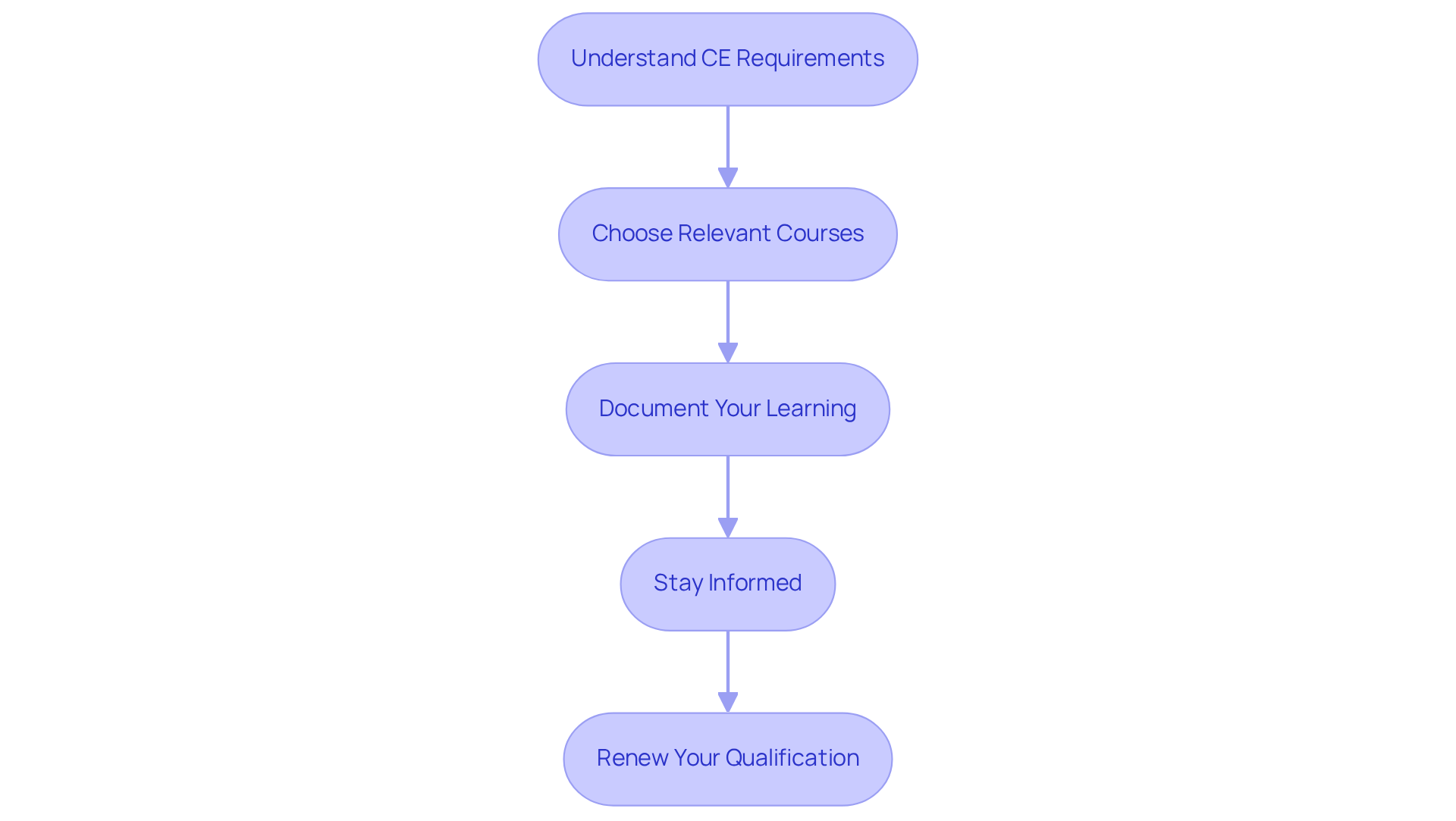
Understand CE Requirements: Each certification has specific continuing education requirements that must be fulfilled within a designated timeframe, typically ranging from 20 to 40 hours every two years. This ongoing education is essential for staying current with evolving treatment practices, ensuring you’re equipped to support those in need.
-
Choose Relevant Courses: Select courses that focus on trauma therapy, ensuring they are taught by a certified trauma therapist and emphasizing new techniques, research, and best practices in trauma-informed care. Programs like the Trauma-Informed Stabilization Treatment (TIST) certification and workshops on Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) can be particularly beneficial. These courses not only enhance your skills but also deepen your understanding of your clients’ experiences.
-
Document Your Learning: Keep thorough records of all completed courses, including certificates of completion and any associated materials. This documentation is vital for your recertification application and demonstrates your commitment to professional development. It’s a tangible reminder of your journey and growth as a therapist.
-
Stay Informed: Join professional organizations related to stress therapy, such as the American Mental Health Counselors Association (AMHCA) or the Association of Traumatic Stress Specialists (ATSS). These organizations provide valuable resources and opportunities for continuing education, fostering a community of informed practitioners. Connecting with others in your field can be incredibly enriching.
-
Renew Your Qualification: Be proactive about renewing your qualification before it expires. Submit your documentation and fees as required by the certifying body to maintain your status. Regular renewal not only ensures compliance but also enhances your skills and effectiveness as a certified trauma therapist. Remember, every step you take in your education is a step towards better supporting your clients.
By committing to ongoing education, you fulfill certification requirements and significantly enhance your therapeutic skills, ultimately leading to better outcomes for your clients. Studies show that trauma-informed care improves client engagement and retention, highlighting the importance of continuous learning in this field. Your dedication to growth not only benefits you but also creates a ripple effect of healing in the lives of those you serve.
Conclusion
Becoming a certified trauma therapist is a deeply rewarding journey, one that equips you with the essential skills to support individuals in emotional distress. This process involves:
- Understanding the certification requirements
- Exploring various types of trauma certifications
- Navigating the application process
- Committing to ongoing education
Each step is vital in building a solid foundation for a fulfilling career in trauma therapy.
Throughout this journey, we highlight key aspects such as:
- The importance of educational qualifications
- Licensure
- Specialized training
The exploration of different certification types, including the Certified Clinical Trauma Professional and Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, showcases the diverse paths available to aspiring therapists. Additionally, grasping the application process and the significance of continuing education ensures that you remain competent and effective in your role.
Ultimately, this journey transcends merely obtaining a certification; it’s about making a meaningful impact in the lives of those who have experienced trauma. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? By pursuing this path with dedication and a commitment to lifelong learning, you can foster healing and resilience in your clients. Embrace this opportunity to transform not only your career but also the lives of those in need of compassionate support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What educational background is required to become a certified trauma therapist?
Most qualifications require at least a master’s degree in a mental health-related field, such as psychology, social work, or counseling. Some qualifications may also welcome individuals currently enrolled in a master’s program.
Is licensure necessary for trauma therapists?
Yes, holding a state or national license in mental health counseling or a related field is crucial. This ensures that you are legally permitted to practice and provide therapy.
Are there specific training programs required for certification?
Yes, many qualifications require you to complete specific training programs focused on trauma-informed care. For example, the Certified Clinical Trauma Professional (CCTP) credential requires finishing a 12-hour training course.
What is the importance of monitored experience in becoming a certified trauma therapist?
Some credentials may require a certain number of guided clinical hours working with clients facing distress. This hands-on experience is vital for developing practical skills and deepening your understanding of clients' needs.
How can understanding these certification requirements help aspiring trauma therapists?
By ensuring you meet these requirements, you can confidently take the next steps toward becoming a certified trauma therapist, enabling you to support others effectively in their healing journey.




