Overview
Trauma can profoundly affect our mental health, sometimes leading to symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). For those predisposed to anxiety disorders, traumatic experiences can heighten anxiety and stress responses, manifesting as obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? You're not alone.
Research shows that approximately 50% of individuals with OCD have experienced distressing events. This statistic emphasizes the importance of recognizing the link between trauma and OCD. Understanding this connection is crucial as it paves the way for targeted treatment approaches that address both trauma and OCD.
As we explore this further, it becomes clear that fostering recovery requires a compassionate approach. Seeking therapy can be a vital step toward healing. Remember, you deserve support and understanding on this journey.
Introduction
Trauma leaves a profound mark on the human psyche, often intertwining with various mental health disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? As individuals navigate the aftermath of distressing experiences, a crucial question emerges: can trauma actually trigger the onset or intensification of OCD symptoms?
This article gently delves into the intricate relationship between trauma and OCD, exploring how emotional distress can manifest as obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. By understanding this connection, readers can uncover vital insights into treatment approaches that address both trauma and OCD, paving the way for healing and recovery. Together, we can embark on a journey toward understanding and support.
Define Trauma and OCD: Key Concepts and Definitions
Trauma can be understood as an emotional response to distressing events, encompassing experiences like abuse, neglect, or natural disasters. These events often leave lasting psychological effects, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? It's important to recognize that such feelings are valid and common.
On the other hand, obsessive-compulsive condition (OCD) manifests through persistent, unwelcome thoughts, known as obsessions, leading individuals to engage in repetitive behaviors, or compulsions, to alleviate their anxiety. Understanding these definitions is vital, as they lay the groundwork for exploring how distress can influence the emergence and severity of OCD symptoms, including the question of whether trauma can cause OCD.
As we delve deeper into this topic, it's essential to acknowledge that healing is possible. Seeking therapy can be a powerful step towards understanding and managing these feelings. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Explore How Trauma Triggers OCD Symptoms
There is evidence to suggest that traumatic events can trauma cause OCD symptoms to significantly activate, particularly in individuals who are already prone to anxiety disorders. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Exposure to distressing experiences often leads to heightened anxiety and stress responses, which may manifest as obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. It's important to recognize that research indicates approximately 50% of individuals with OCD have experienced distressing events, which raises the question: can trauma cause OCD?
The pressure of distress can create a strong desire for control, prompting individuals to engage in compulsive actions as a coping strategy. This relationship underscores the importance of addressing emotional distress in the treatment of OCD. As we explore this further, it becomes clear that understanding these connections can be a vital step towards healing. Seeking therapy can provide the support needed to navigate these challenges and foster a sense of control and peace in your life.
Examine Treatment Approaches for Trauma-Induced OCD
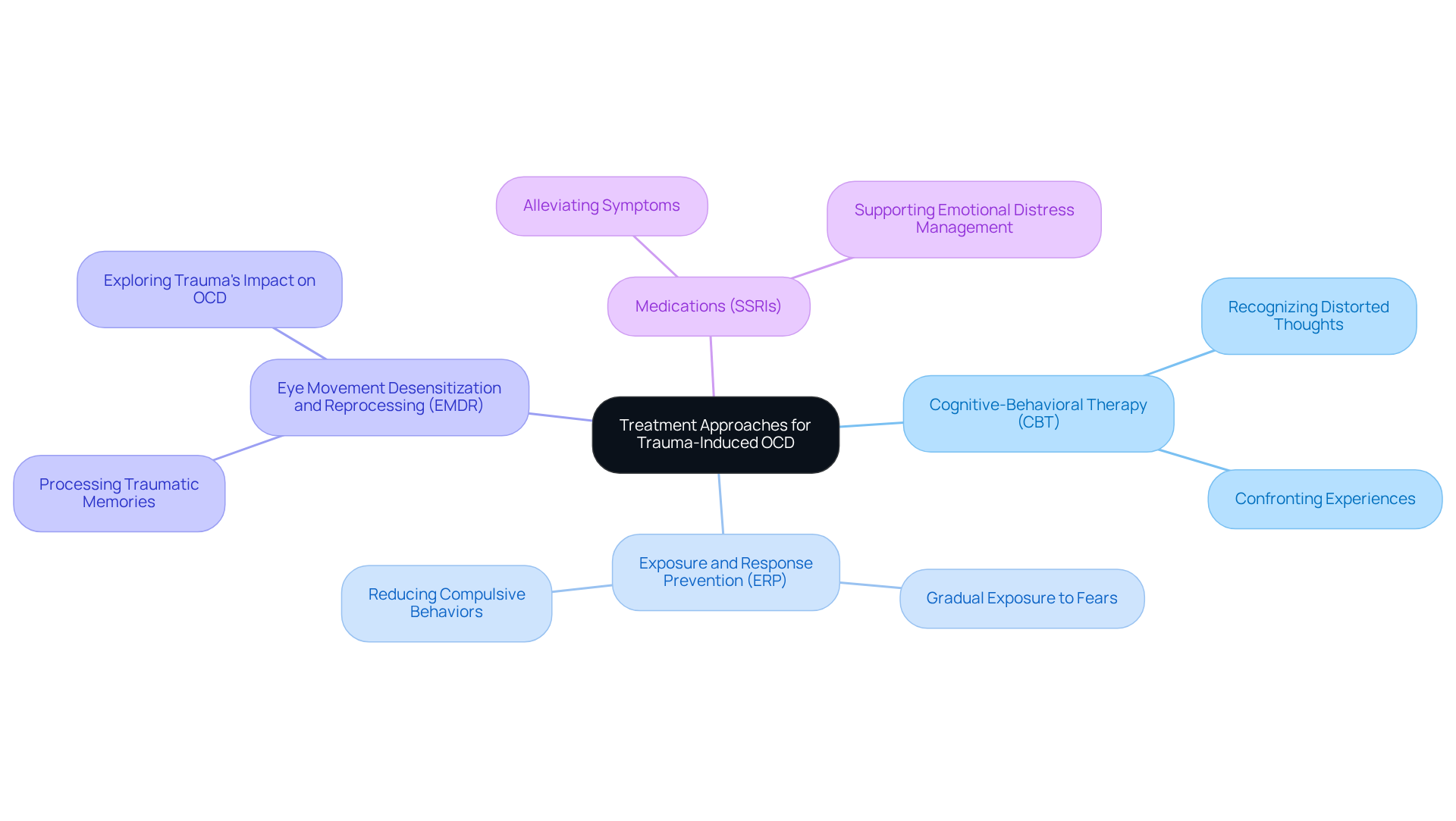
Understanding whether trauma can cause OCD is crucial, as treatment for trauma-induced OCD often involves a compassionate blend of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention (ERP). CBT helps individuals recognize and confront the distorted thoughts that can arise from their experiences and OCD. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? ERP gradually exposes individuals to anxiety-inducing situations, allowing them to face their fears without resorting to compulsive behaviors.
In addition to these approaches, trauma-focused therapies such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) can be incredibly beneficial for processing traumatic memories and exploring how trauma can cause OCD. Medications, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may also be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms. A thorough treatment strategy that addresses both emotional distress and OCD is crucial for successful recovery. Remember, seeking help is a brave step towards healing.
Understand the Broader Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
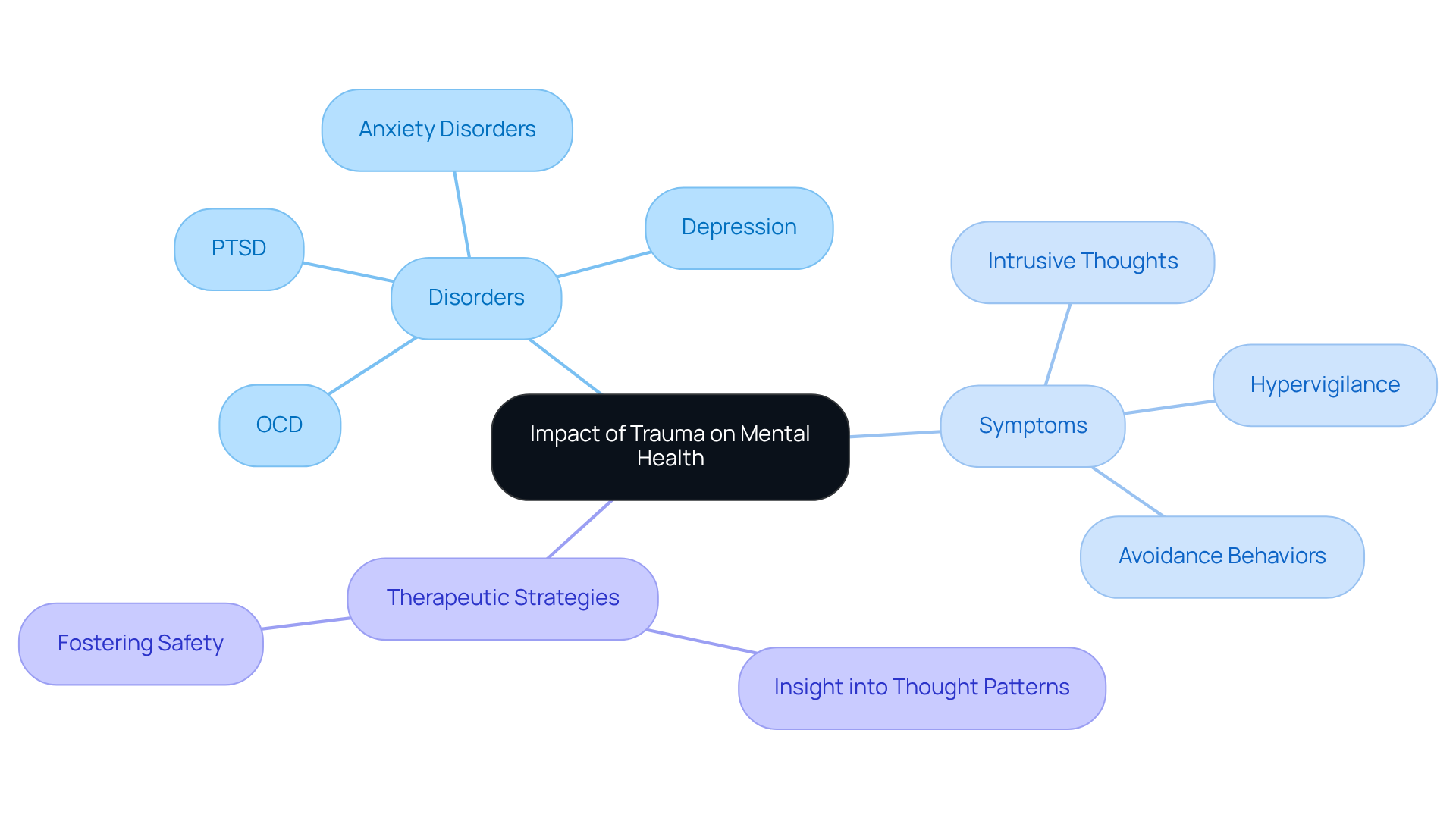
Trauma can profoundly affect mental health, leading to various disorders, and raises the question of whether trauma can cause OCD, as it also contributes to conditions like PTSD, depression, and anxiety disorders. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Those who have faced distress may feel haunted or immobilized by their history, struggling with emotional control that complicates relationships and daily functioning.
The nervous system often acts as an emergency alarm, which can become dysregulated during traumatic experiences. This dysregulation may manifest as intrusive thoughts, hypervigilance, and avoidance behaviors, making recovery feel like an uphill battle. At The Emerald Couch, we understand that with the right support, it is possible to reduce the impact of OCD and other trauma-related symptoms.
Our therapeutic strategies focus on helping individuals gain greater insight into their patterns of thought and behavior, ultimately fostering safety in their bodies, homes, and lives. Understanding the broader implications of trauma, especially regarding the question of how trauma can cause OCD, is crucial for mental health professionals, as it highlights the importance of comprehensive treatment approaches that address the multifaceted nature of trauma-related disorders. Together, we can embark on a journey toward healing and restoration.
Conclusion
The relationship between trauma and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) reveals a complex interplay that highlights the importance of understanding both conditions. The emotional aftermath of traumatic experiences can lead to heightened anxiety and stress, potentially triggering or worsening OCD symptoms in those who are vulnerable. Recognizing this connection is crucial for fostering awareness and encouraging those affected to seek help.
Research indicates that approximately 50% of individuals with OCD report having experienced distressing events, suggesting a strong link between trauma and the emergence of obsessive-compulsive behaviors. Treatment approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure and response prevention (ERP) are vital in addressing trauma-induced OCD. Additionally, trauma-focused therapies and medications can further support recovery, underscoring the need for a comprehensive treatment strategy.
Ultimately, understanding how trauma impacts mental health and contributes to disorders like OCD is essential for both individuals and mental health professionals. By acknowledging the broader implications of trauma, it becomes evident that seeking help is not only a courageous step but also a necessary one on the journey to healing. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Embracing therapeutic support can empower individuals to reclaim control over their lives, fostering a sense of safety and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is trauma?
Trauma is an emotional response to distressing events such as abuse, neglect, or natural disasters, which can lead to lasting psychological effects like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress.
How can trauma affect individuals?
Trauma can leave individuals feeling overwhelmed by their past, and such feelings are valid and common. It often leads to lasting psychological effects that require attention and healing.
What is obsessive-compulsive condition (OCD)?
OCD is characterized by persistent, unwelcome thoughts called obsessions, which drive individuals to engage in repetitive behaviors known as compulsions to alleviate their anxiety.
Why is it important to understand the definitions of trauma and OCD?
Understanding the definitions of trauma and OCD is vital as it lays the groundwork for exploring how distress can influence the emergence and severity of OCD symptoms, including the potential link between trauma and OCD.
Can trauma cause OCD?
The article suggests exploring the relationship between trauma and OCD symptoms, indicating a potential link, although it does not provide a definitive answer.
What steps can individuals take to manage feelings related to trauma and OCD?
Seeking therapy is highlighted as a powerful step towards understanding and managing feelings related to trauma and OCD, emphasizing that healing is possible and individuals are not alone in their journey.




