Overview
Existential anxiety can often leave individuals with a profound sense of unease, stirring deep questions about existence, mortality, and personal identity. It's crucial to recognize this as a valid mental health issue, one that deserves attention to prevent more serious emotional challenges. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by thoughts of your own existence? This feeling is not uncommon, and acknowledging it is the first step towards healing.
The article emphasizes the significance of tailored therapeutic approaches, such as existential therapy and mindfulness practices. These methods can gently guide individuals through their feelings of dread, fostering personal growth and understanding. As we explore this further, it's essential to address this anxiety effectively, allowing for a journey towards emotional well-being.
By seeking support, you can navigate these challenging feelings and find a path that resonates with your personal journey. Remember, you are not alone in this experience, and there are compassionate resources available to help you thrive.
Introduction
In a world where profound questions about existence often loom large, existential anxiety emerges as a significant yet often overlooked mental health concern. This type of anxiety arises from deep reflections on life’s meaning, the inevitability of death, and the essence of personal identity—especially during times of transition or crisis.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by these thoughts? As individuals grapple with these existential dilemmas, they may find themselves caught in a cycle of worry and emotional distress, disrupting their daily lives. Understanding the nuances of existential anxiety is essential for fostering resilience and personal growth.
This article delves into the characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options for existential anxiety, shedding light on how individuals can navigate their emotional landscapes and seek meaningful support in the face of life's uncertainties. Together, we can explore these feelings and find pathways to healing.
Define Existential Anxiety and Its Importance
Existential anxiety can be described as a profound sense of unease or dread that arises from deep contemplation of fundamental questions, such as the meaning of existence, the inevitability of death, and the nature of personal identity. This type of apprehension often surfaces during significant life changes or crises, prompting individuals to confront their mortality and the inherent limitations of their lives.
Recognizing this fundamental distress as a valid mental health issue is crucial, as it can lead to more serious emotional and psychological difficulties if overlooked. For instance, the DASS-21 scale evaluates symptoms of depression, worry, and stress, highlighting the prevalence of significant distress among various groups. This suggests that such feelings are widespread and can greatly impact mental health. In particular, students facing academic pressures frequently report feelings of meaninglessness, underscoring the need for targeted therapeutic approaches.
As noted by Haneen Al Shehri, "This study is the first to explore EA among undergraduate students in Saudi Arabia," emphasizing the importance of addressing this issue within specific demographics.
Addressing existential anxiety in therapy is of utmost importance. Therapeutic modalities, such as dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), have shown promise in helping individuals navigate these feelings, fostering resilience and personal growth. Mindfulness practices, woven into therapy, can enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation, allowing individuals to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment.
This approach can be particularly beneficial for trauma survivors, as it helps them slow down and create space between themselves and their experiences, ultimately leading to a deeper understanding of their emotional landscapes.
A notable case study on psychedelic therapy for stress revealed that substances like psilocybin and LSD led to significant reductions in symptoms, with effects lasting up to a year. This indicates that innovative therapeutic options may offer relief for those grappling with fundamental concerns, especially regarding feelings of meaninglessness.
By recognizing and examining fundamental distress, individuals can gain valuable insights into their emotional landscapes, empowering them to address and seek appropriate support and interventions. This proactive approach not only alleviates distress but also fosters a deeper understanding of oneself amidst uncertainties.
Differentiate Existential Thoughts from Other Anxiety Types
This sense of dread is distinct from other forms of unease, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder, primarily because it embodies existential anxiety, focusing on themes of existence. GAD is characterized by excessive worry about various aspects of life, whereas profound worry often reflects existential anxiety tied to deep questions about existence, purpose, and mortality. Have you ever found yourself pondering, 'What is the purpose of life?' or 'What happens after death?' Such reflections can lead to feelings of despair and hopelessness, starkly contrasting with the more generalized existential anxiety associated with GAD.
Research indicates that profound apprehension can manifest uniquely, with studies showing it accounts for variations in beliefs about justice and well-being beyond personal differences in long-term goals and fear of death. This suggests that individuals grappling with existential anxiety may face a deeper emotional struggle that shapes their perspective, setting it apart from the more situational concerns seen in GAD and the intense fear responses typical of panic disorder. For instance, while panic disorder can trigger sudden, intense fear reactions, profound unease emerges as a persistent, underlying worry that may influence daily functioning and emotional health.
Understanding these differences is vital for effective therapeutic approaches. Tailored treatment methods, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and existential therapy, can help individuals explore their emotions surrounding existential anxiety and mortality. Integrating mindfulness practices into these therapeutic approaches can significantly enhance emotional regulation and personal growth.
Mindfulness techniques, including meditation and attentive breathing, allow individuals to reflect on their thoughts and emotions without judgment, creating a nurturing space to address fundamental issues more effectively. For example, case studies illustrate that working with a therapist can lead to a deeper understanding of profound worries, enabling individuals to manage their emotions more successfully, fostering personal growth and acceptance. One such case study highlights how therapy, combined with mindfulness techniques, helped a client articulate their fears about death, resulting in a greater sense of peace and acceptance.
Moreover, individuals with high self-worth, as noted by Spencer et al., tend to view themselves positively across various domains, which may provide them with additional psychological resources when facing fundamental concerns. By recognizing the unique characteristics of profound distress and incorporating mindfulness practices, such as breath awareness and body scans, therapists can offer essential support to help clients navigate their significant concerns, , and cultivate resilience.
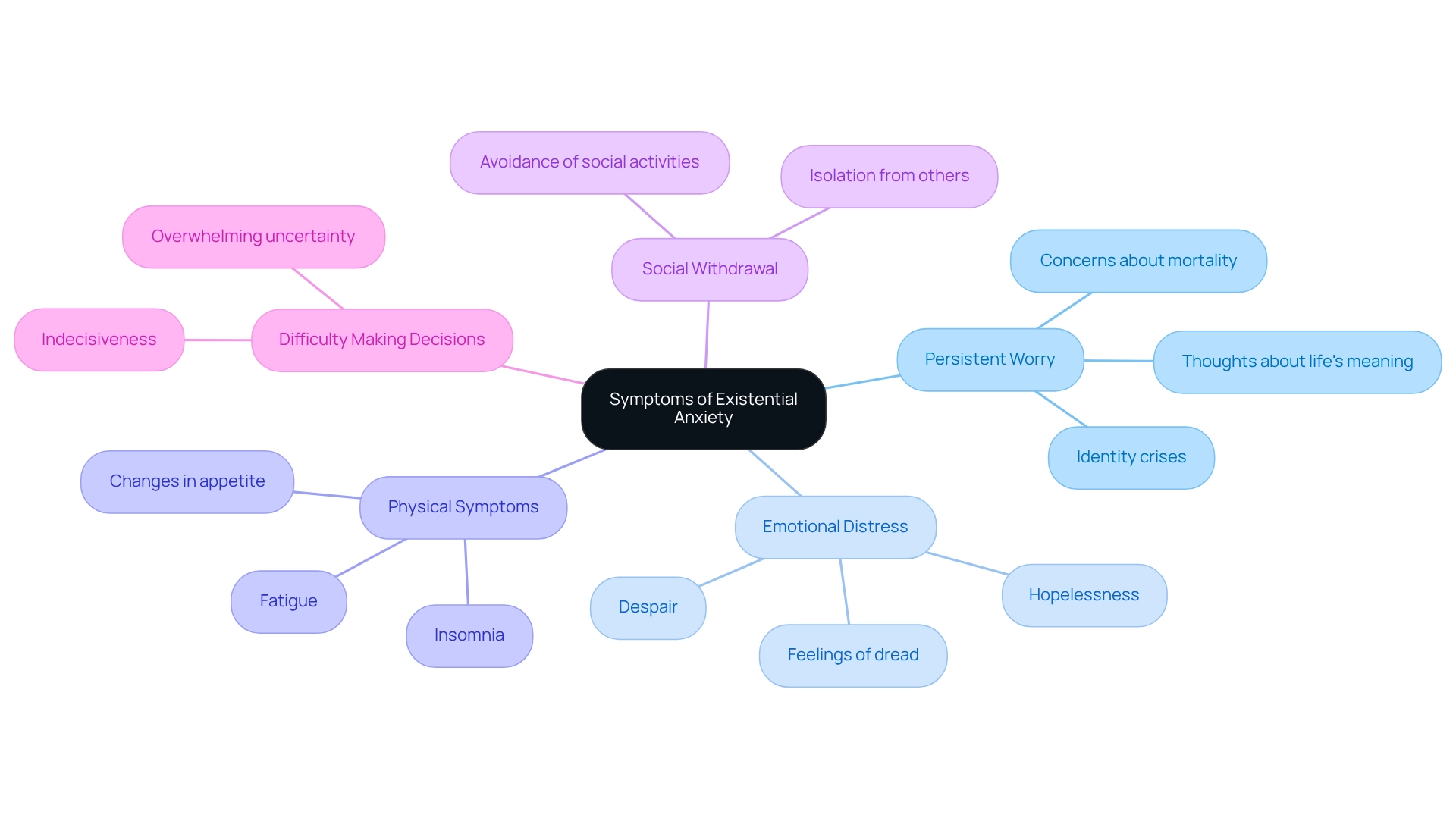
Identify Symptoms of Existential Anxiety
Recognizing signs of existential anxiety is essential for individuals seeking to understand . Common manifestations include:
- Persistent Worry: Have you ever found yourself caught in frequent thoughts about life's meaning, mortality, and your personal identity? This can lead to a cycle of anxiety that feels overwhelming.
- Emotional Distress: Feelings of dread, hopelessness, or despair can significantly disrupt your daily functioning, making it challenging to engage in routine activities that once brought you joy.
- Physical Symptoms: Chronic worry may manifest as fatigue, insomnia, or changes in appetite, highlighting the profound connection between mind and body in stress-related disorders.
- Social Withdrawal: Many individuals find themselves withdrawing from social situations or activities they once enjoyed, often driven by feelings of isolation or disconnection from others.
- Difficulty Making Decisions: Overwhelming uncertainty can lead to indecisiveness, complicating choices and contributing to further stress.
Recognizing these symptoms is a vital first step in initiating the healing process. Research suggests that emotional turmoil related to fundamental concerns is widespread, with many adults reporting significant effects on their daily routines. For instance, a study found that 65% of psychiatric residents in the United States grappled with philosophical, conceptual, and metaphysical challenges related to psychiatry, underscoring the pervasive nature of these concerns.
Reliable measurement tools like the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS) and the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) have confirmed the validity of these symptoms, with a goodness-of-fit index showing RMSEA=0.07. This highlights the importance of seeking professional help. At The Emerald Couch, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to better understand your needs and tailor our services to support your journey.
Our therapeutic process begins with an intake session where we gather necessary information to collaboratively develop your custom treatment plan, ensuring that we address your specific symptoms and goals. As Vara Saripalli, Psy.D., observes, "While a person may experience existential anxiety as overwhelming at times, it does not have to dominate one’s life." By understanding and acknowledging these signs, you can take the first steps toward recovery and personal growth.
Steven Hayes further emphasizes that "worry is not a sign of sickness, a weakness of the mind or an error for which we should always seek a medical solution." This perspective aligns with the therapeutic approach of The Emerald Couch, which encourages clients to confront their past while focusing on future possibilities.
Explore Treatment Options for Existential Anxiety
Effective treatment options for profound distress encompass a variety of therapeutic methods designed to address the unique challenges individuals face.
Existential Therapy invites individuals to confront their existential anxiety, nurturing personal growth and resilience. By exploring themes of significance and intention, clients can gain deeper insights into their experiences and develop effective coping strategies.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is celebrated for its flexibility, assisting individuals in reshaping negative thought patterns associated with existential anxiety. Its structured approach fosters healthier coping techniques, empowering clients to manage their stress effectively.
Mindfulness and Meditation practices, integrated at The Emerald Couch, ground individuals in the present moment, significantly alleviating stress linked to future uncertainties. These methods enhance emotional regulation and reduce stress symptoms, serving as invaluable resources for those facing existential anxiety. They not only improve self-awareness but also encourage personal development, making them essential components of therapeutic practices for trauma and stress recovery.
Support Groups offer a nurturing environment where individuals can connect with others who share similar experiences, fostering a sense of community and understanding that diminishes feelings of isolation. These groups provide emotional support and shared coping strategies, enriching .
Medication may be considered in instances where anxiety symptoms are severe, aiding in the management of these challenges. While not a standalone solution, medication can be a valuable part of a comprehensive treatment plan, allowing individuals to engage more fully in their therapeutic processes.
Exploring these treatment options empowers individuals to take charge of their mental health, paving the way toward a more fulfilling life. As ongoing research continues to refine these approaches, the effectiveness of therapies like CBT and existential therapy remains a focal point in the pursuit of improved mental health outcomes. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Consider reaching out for support—your journey toward healing can begin today.
Conclusion
Existential anxiety is a significant mental health concern that often emerges from deep reflections on life’s meaning, mortality, and identity, particularly during pivotal transitions. Recognizing it as a legitimate issue is essential; neglecting these feelings can lead to more severe emotional challenges. Therapeutic approaches—such as dialectical behavioral therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy—offer valuable tools for navigating these complex emotions and fostering resilience.
Distinguishing existential anxiety from other types, like generalized anxiety disorder, is crucial for effective treatment. While generalized anxiety involves excessive worries about daily life, existential anxiety delves into profound questions about existence and purpose. Identifying symptoms like persistent worry and emotional distress empowers individuals to seek appropriate support and embark on their healing journey.
A range of treatment options—including existential therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, and support groups—provides individuals with the means to manage existential anxiety effectively. These approaches not only enhance emotional regulation but also promote personal growth.
Ultimately, confronting existential anxiety can lead to meaningful insights and a deeper connection to oneself and the world. By engaging with professional support and therapeutic practices, individuals can transform existential anxiety from a source of distress into an opportunity for growth and self-discovery, fostering resilience and finding meaning amidst life’s uncertainties. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Remember, you are not alone, and seeking help can be the first step toward a more fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is existential anxiety?
Existential anxiety is a profound sense of unease or dread that arises from deep contemplation of fundamental questions, such as the meaning of existence, the inevitability of death, and the nature of personal identity.
When does existential anxiety typically arise?
This type of anxiety often surfaces during significant life changes or crises, prompting individuals to confront their mortality and the inherent limitations of their lives.
Why is it important to recognize existential anxiety as a mental health issue?
Recognizing existential anxiety as a valid mental health issue is crucial because it can lead to more serious emotional and psychological difficulties if overlooked.
What tools are used to evaluate existential anxiety and its symptoms?
The DASS-21 scale is used to evaluate symptoms of depression, worry, and stress, highlighting the prevalence of significant distress among various groups.
Who is particularly affected by feelings of meaninglessness related to existential anxiety?
Students facing academic pressures frequently report feelings of meaninglessness, indicating a need for targeted therapeutic approaches.
What therapeutic modalities are effective in addressing existential anxiety?
Therapeutic modalities such as dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) have shown promise in helping individuals navigate feelings of existential anxiety.
How can mindfulness practices benefit those experiencing existential anxiety?
Mindfulness practices can enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation, allowing individuals to observe their thoughts and feelings without judgment, which is particularly beneficial for trauma survivors.
What innovative therapeutic options have shown effectiveness in reducing existential anxiety symptoms?
Psychedelic therapy using substances like psilocybin and LSD has led to significant reductions in symptoms of existential anxiety, with effects lasting up to a year.
How can individuals address their existential anxiety?
By recognizing and examining their fundamental distress, individuals can gain valuable insights into their emotional landscapes, empowering them to seek appropriate support and interventions.




