Overview
This article delves into the experiences and implications of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), shedding light on its symptoms, historical context, personal narratives, and emotional impact. It underscores the importance of awareness and support for individuals living with OCD.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Many effective treatments are available, yet countless individuals hesitate to seek help due to the stigma and misunderstanding surrounding this condition. This reluctance can profoundly affect their quality of life, making it essential for us to foster a compassionate understanding of OCD and encourage those affected to reach out for support.
Introduction
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition that affects millions globally, yet its complexities often remain misunderstood.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past?
By delving into the stories of those living with OCD, readers can gain valuable insights into the daily struggles and triumphs that accompany this disorder.
However, with a staggering number of individuals never seeking treatment, we must ask ourselves: how can society better support those grappling with OCD?
It is essential to foster a deeper understanding of its profound impact on emotional and psychological well-being. Together, we can create a nurturing environment that encourages healing and connection.
Define Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Key Concepts and Importance
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a complex mental health condition characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts known as obsessions, alongside repetitive behaviors or mental acts referred to as compulsions. Individuals often feel a strong urge to perform these compulsions in response to their obsessions, which can lead to significant anxiety and distress. For instance, have you ever felt overwhelmed by the need to wash your hands repeatedly due to fears of contamination? This is a common experience for someone with an obsession about cleanliness, who may wash their hands excessively, sometimes for hours each day, in an effort to alleviate their fears.
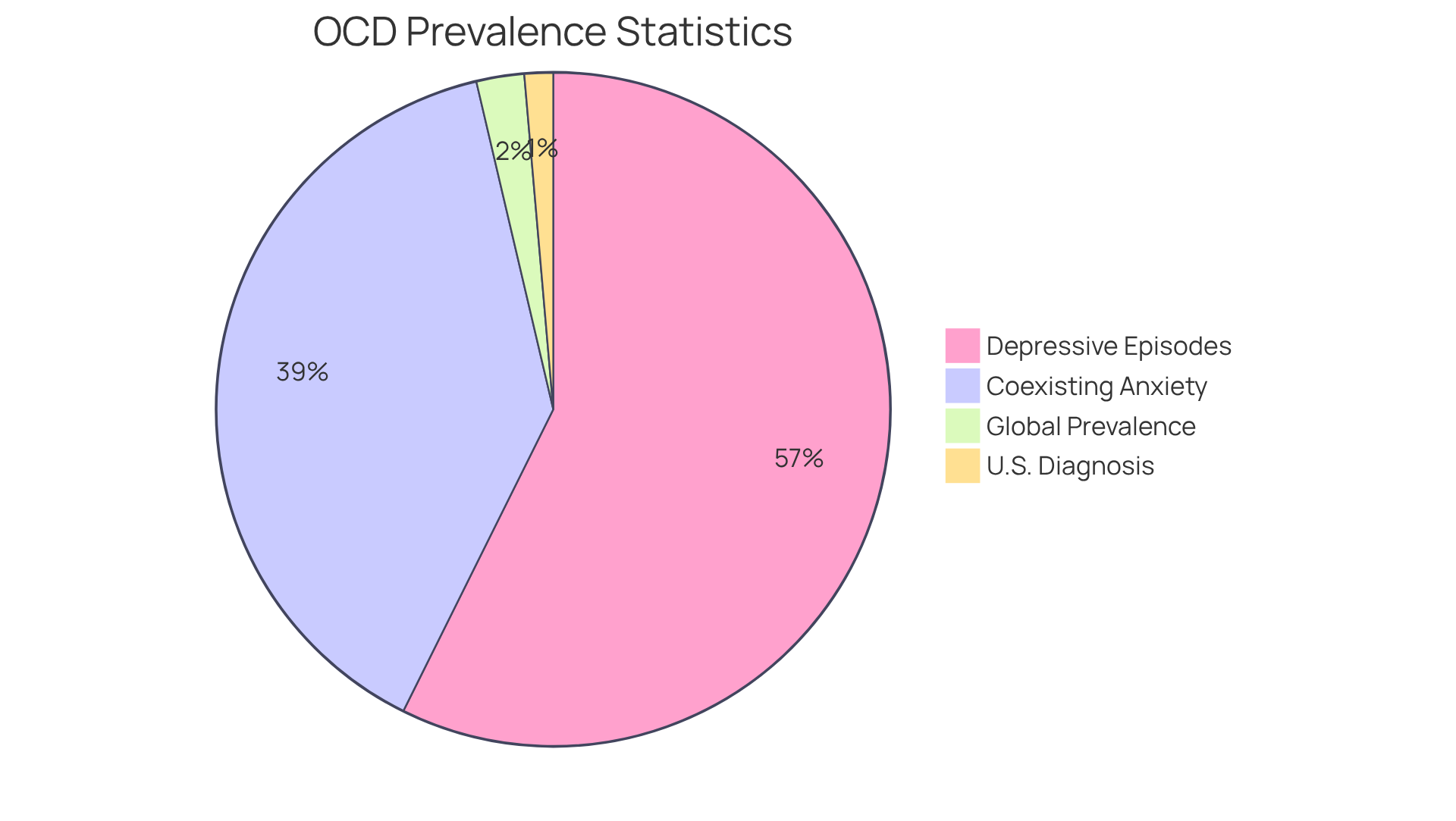
Understanding the stories of obsessive compulsive disorder is crucial, as , translating to millions of individuals worldwide. In the United States, around 1.2% of adults, or 2.5 million people, are diagnosed with OCD. The disorder can severely disrupt daily functioning, with symptoms consuming over an hour of a person's day, impacting their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in everyday activities. Additionally, up to 34% of those with OCD may also experience a coexisting anxiety disorder, while around 50% encounter a significant depressive episode at some point in their lives. This highlights the interconnected nature of psychological health challenges and the [importance of seeking help](https://blog.theemeraldcouch.com/understanding-the-role-of-a-trauma-specialist-in-healing).
The impact described in stories of obsessive compulsive disorder on quality of life is profound, with many individuals experiencing substantial distress and impairment in both personal and professional spheres. Raising awareness and fostering understanding of OCD are essential steps in reducing stigma and encouraging those affected to seek professional support. Evidence-based treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can significantly alleviate the burden of this disorder. As noted by the American Psychiatric Association, "Compulsions are repetitive actions or cognitive acts that the individual feels compelled to carry out in reaction to their obsession or by rigorously enforced rules." If you or someone you know is struggling with OCD, remember that you are not alone, and help is available.
Trace the Historical Development of OCD: From Misunderstanding to Recognition
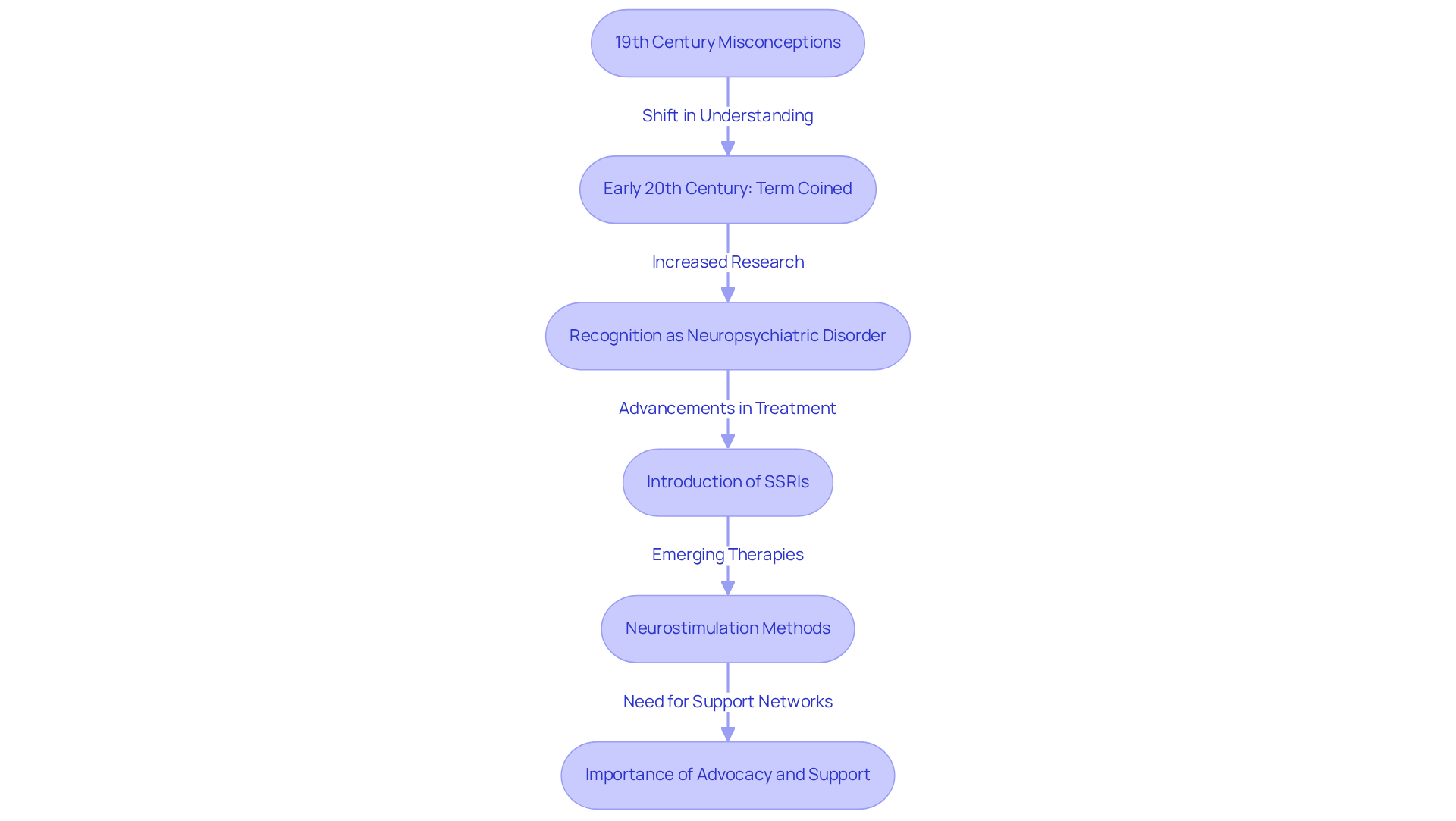
The understanding of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) has undergone a profound transformation since its initial descriptions in the 19th century, when symptoms were often misattributed to moral or religious shortcomings. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? The phrase 'obsessive-compulsive disorder' emerged in the early 20th century, but it wasn't until the latter half of the century that OCD began to be recognized as a distinct psychological condition. This shift was propelled by extensive research and clinical observations that established OCD as a neuropsychiatric disorder. As we explore this further, we see the development of refined diagnostic criteria, including those outlined in the ICD-10 and DSM-5, which have led to enhanced treatment options.
Notably, the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), particularly fluvoxamine, marked a significant advancement in the pharmacological treatment of OCD. Furthermore, neurostimulation methods like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) have shown promise for treatment-resistant cases. Despite these advancements, it is vital to acknowledge that 55% of adults experiencing a psychological condition never pursue treatment. This statistic highlights the importance of in promoting psychological well-being.
Support networks play a crucial role in the recovery journey for individuals with OCD, emphasizing the need for a compassionate approach. The historical trajectory of OCD underscores the essential need for continuous advocacy and education in mental health. It is our hope that those affected by this condition receive the understanding and support they truly deserve. Let us come together to foster a community that nurtures healing and encourages seeking help.
Explore Personal Narratives: Real Stories of Living with OCD
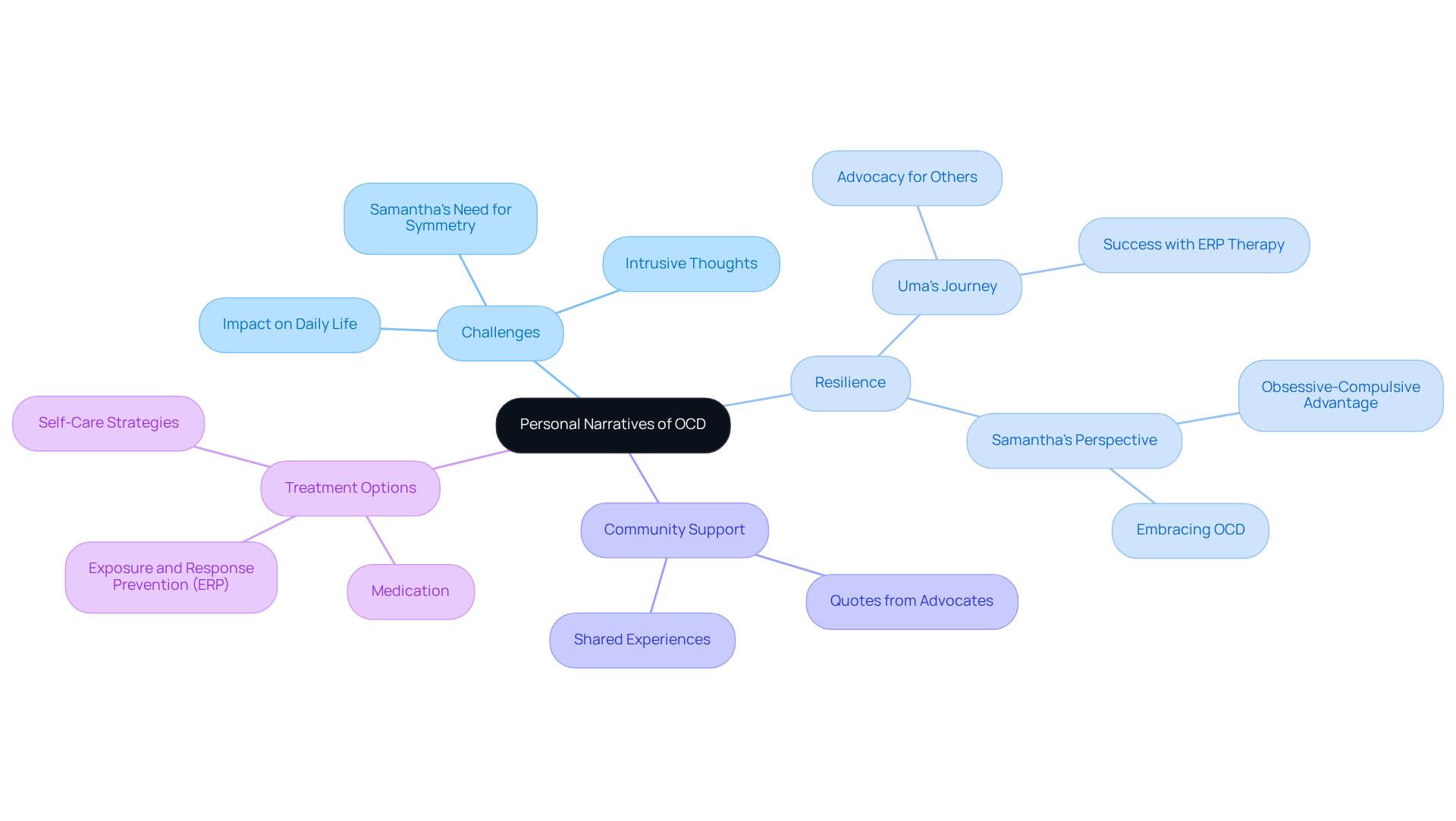
Personal stories of obsessive compulsive disorder from individuals reveal the profound impacts that these stories of obsessive compulsive disorder have on daily life. For example, Samantha Pena, a mathematics teacher, shares her journey with the need for symmetry and perfectionism, which shapes her daily routines and tasks. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by such demands?
Another individual might recount their battle with intrusive thoughts about harming loved ones, leading to compulsive checking behaviors that disrupt their everyday activities. These stories of obsessive compulsive disorder highlight not only the challenges posed by OCD, such as excessive hand washing and checking, but also celebrate the resilience and potential for recovery among those affected.
As Uma Chatterjee, a neuroscience researcher and advocate for individuals with OCD, compassionately states, "Know that you're not alone." Sharing these experiences fosters a sense of community and hope, reminding everyone that they are not isolated in their struggles.
Research shows that approximately 70% of people with OCD respond positively to treatment options like exposure and response prevention (ERP) therapy. This emphasizes the importance of personal stories of obsessive compulsive disorder in motivating others to seek help and embrace their healing journey. Together, we can and find support in our shared experiences.
Examine the Impact of OCD: Emotional and Psychological Challenges
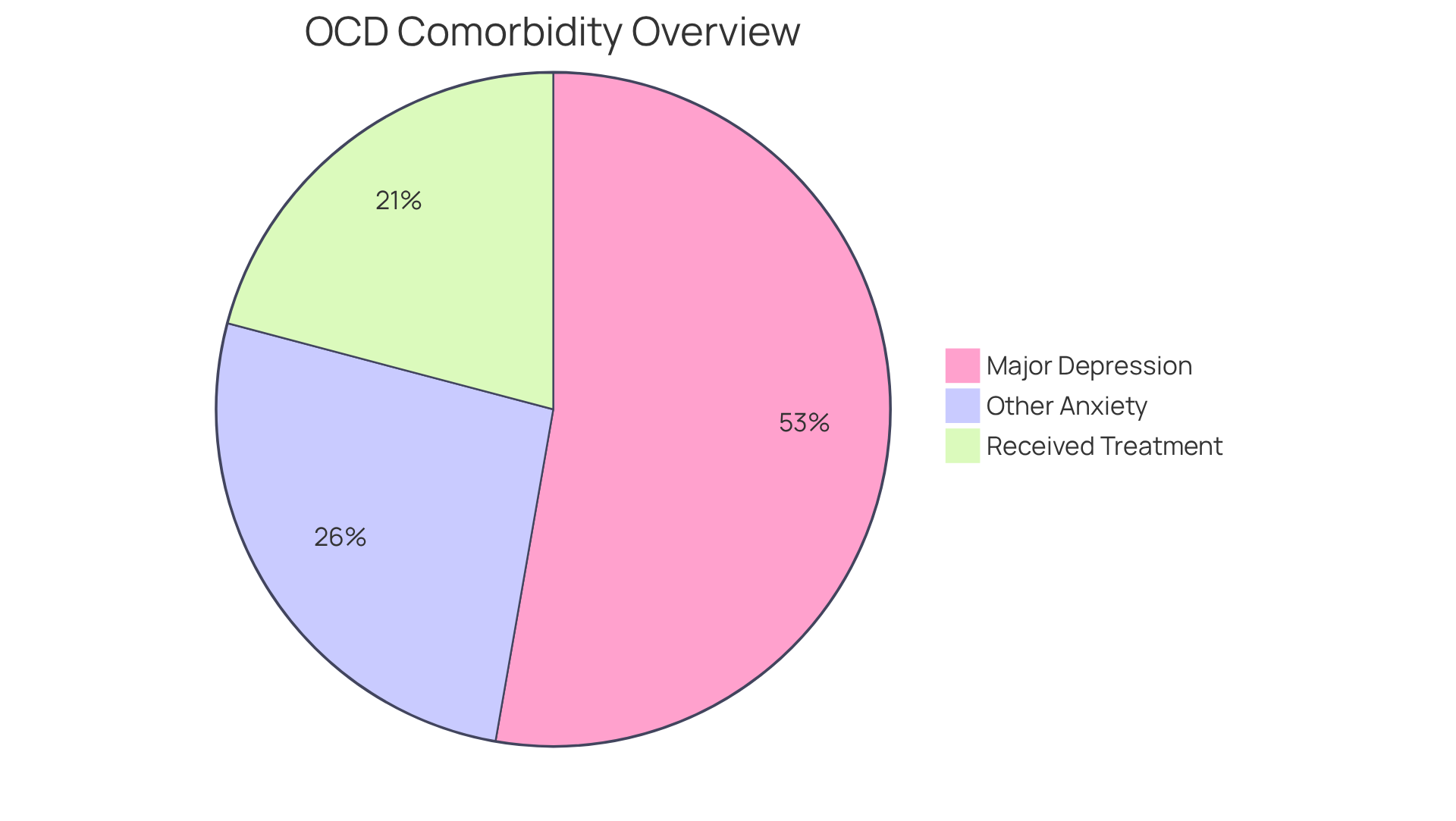
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can deeply affect emotional and psychological well-being, often leading to increased feelings of anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by these emotions? Studies reveal that approximately 50% of individuals with OCD also experience major depressive disorder, while around 25% contend with other anxiety disorders. This overlap can complicate treatment, as the presence of comorbid conditions may intensify OCD symptoms and hinder recovery efforts.
The stigma surrounding psychological disorders often exacerbates feelings of shame and isolation for those living with OCD. Many individuals may take years to recognize their symptoms and seek help. Research indicates that it can take an average of 14 to 17 years to receive a proper diagnosis after symptoms first appear. This delay not only prolongs distress but also increases the likelihood of developing additional psychological issues. Alarmingly, only 19.8% of individuals with OCD received any form of treatment in the past year, highlighting a significant treatment gap.
Psychologists emphasize that OCD can create a profound sense of uncertainty and anxiety, which may alienate individuals from their social circles. Dr. Boduryan-Turner shares, "OCD greatly affects a person’s life due to intrusive thoughts, anxiety, and uncertainty." The World Health Organization recommends relaxation techniques, such as meditation and yoga, along with support groups as valuable resources for those affected by OCD. These approaches underscore the importance of fostering a nurturing environment that encourages open conversations about mental wellness.
Understanding the , along with the stories of obsessive compulsive disorder and its comorbid conditions, is crucial for developing effective treatment plans. As we explore this further, it becomes clear that by creating a compassionate and inclusive atmosphere, mental health professionals can empower individuals to navigate their unique challenges. This support ultimately helps them reclaim their lives and enhance their overall well-being.
Conclusion
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a multifaceted mental health condition that significantly impacts individuals' lives through persistent obsessions and compulsions. Understanding the complexities of OCD is vital, as it affects millions worldwide, leading to distress and impairment in daily functioning. By recognizing the nature of OCD, have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Individuals can better grasp the challenges faced by those living with the disorder and the importance of seeking help.
As we explore this further, the article delves into the definition of OCD, its historical evolution from misunderstanding to recognition, and the personal narratives that illustrate the emotional and psychological challenges faced by those affected. Key insights include:
- The prevalence of comorbid conditions
- The stigma surrounding mental health
- The necessity of effective treatments like cognitive-behavioral therapy
These elements underscore the critical need for awareness and support within communities to foster understanding and reduce stigma.
Ultimately, the journey toward understanding OCD is not just about recognizing the disorder itself but also about acknowledging the human experiences behind it. Advocating for mental health awareness, encouraging open conversations, and supporting those affected can create a more compassionate society. It is essential to remember that help is available and that individuals do not have to navigate their struggles alone. Together, fostering a supportive environment can empower those with OCD to reclaim their lives and pursue healing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)?
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts known as obsessions, and repetitive behaviors or mental acts called compulsions. Individuals feel a strong urge to perform these compulsions in response to their obsessions, which can lead to significant anxiety and distress.
How common is OCD?
OCD affects approximately 1-2% of the global population, which translates to millions of individuals worldwide. In the United States, around 1.2% of adults, or about 2.5 million people, are diagnosed with OCD.
What impact does OCD have on daily life?
OCD can severely disrupt daily functioning, with symptoms consuming over an hour of a person’s day. This can impact their ability to work, maintain relationships, and engage in everyday activities.
Are there any coexisting conditions associated with OCD?
Yes, up to 34% of individuals with OCD may also experience a coexisting anxiety disorder, and around 50% may encounter a significant depressive episode at some point in their lives.
Why is it important to understand OCD?
Understanding OCD is crucial as it raises awareness, reduces stigma, and encourages those affected to seek professional support. The disorder can lead to substantial distress and impairment in both personal and professional areas of life.
What treatments are available for OCD?
Evidence-based treatments, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can significantly alleviate the burden of OCD. Seeking help from professionals is important for those struggling with the disorder.




