Introduction
Understanding the deep connection between trauma and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can profoundly affect mental health, often in ways that go unnoticed. Did you know that around 60% of individuals with OCD may experience symptoms tied to traumatic events? This highlights the urgent need for awareness and effective treatment.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Navigating the complexities of trauma-induced OCD can be challenging, but there are strategies available to help foster healing. In this article, we’ll explore the symptoms, treatment options, and the essential need for trauma-informed approaches to address this difficult condition. Together, we can work towards understanding and healing.
Define Trauma and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Trauma can deeply affect our emotional well-being. It often arises from distressing events like abuse, neglect, or natural disasters, leading to long-lasting psychological effects such as anxiety and depression. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Recent studies reveal that around 60% of individuals with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) developed trauma induced OCD following a stressful life event. This highlights just how significant distress can be on our mental health.
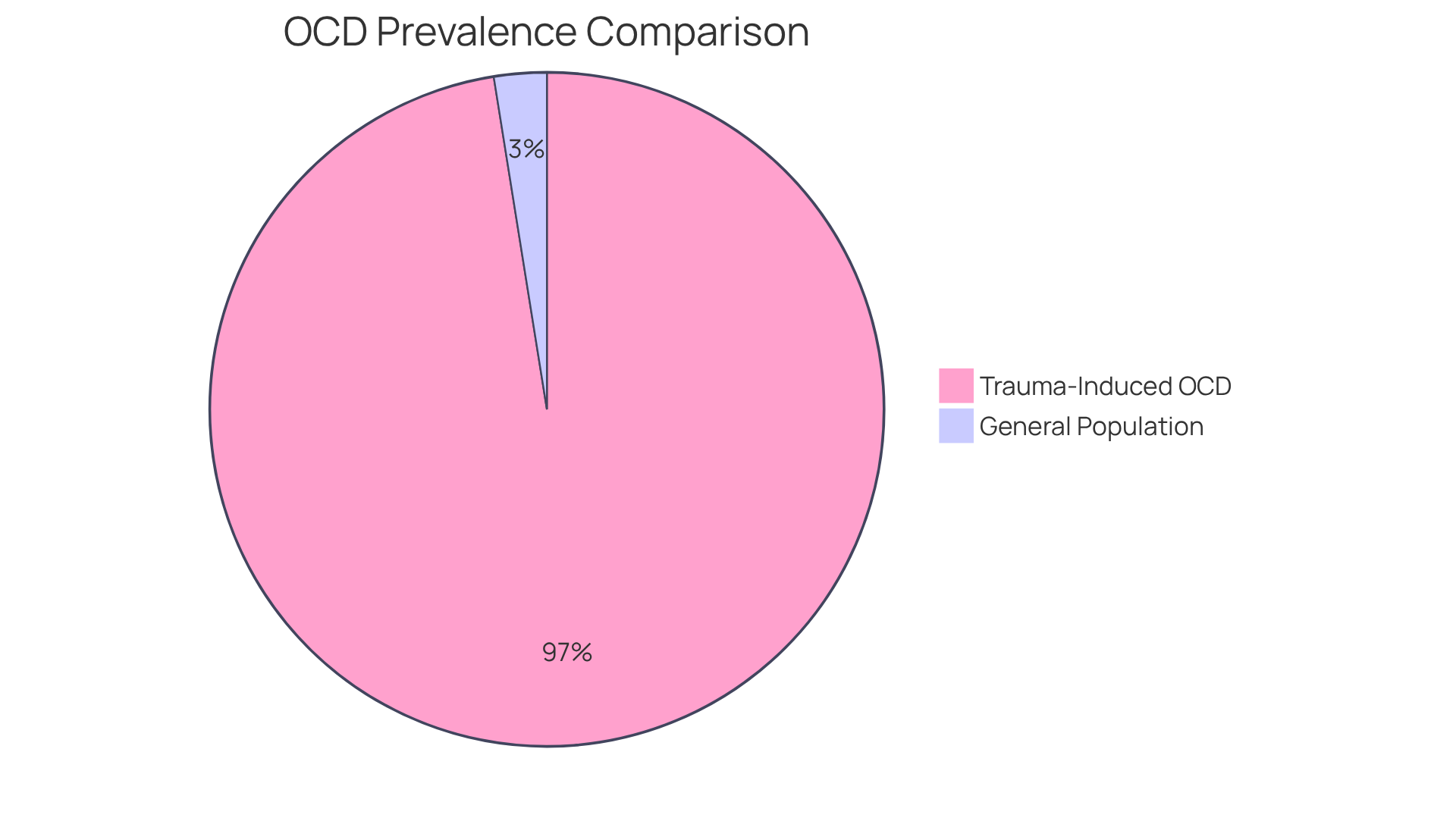
OCD is characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts - known as obsessions - and repetitive behaviors, or compulsions, that individuals feel compelled to perform in response to these thoughts. The connection between distress and OCD is profound. Research indicates that the prevalence of trauma induced OCD among individuals with a traumatic background ranges from 30% to 82%, starkly contrasting with a general population prevalence of only 1.1 - 1.8%.
Understanding these definitions and their interrelation is crucial. It sheds light on how distress can trigger the emergence of trauma induced OCD. Real-world instances show us that distressing experiences can indeed lead to symptoms of trauma induced OCD. If you or someone you know is struggling, remember that seeking help is a brave step towards healing. You don’t have to navigate this journey alone.
Explore the Link Between Trauma and OCD Development
Research shows a strong link between traumatic experiences and the onset of trauma induced OCD. Trauma can lead to trauma induced OCD, disrupting how our brains function and how we respond to stress, which results in increased anxiety and intrusive thoughts. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Many people who have faced significant distress often find themselves turning to compulsive behaviors as a way to cope with their heightened anxiety, potentially developing trauma induced OCD.
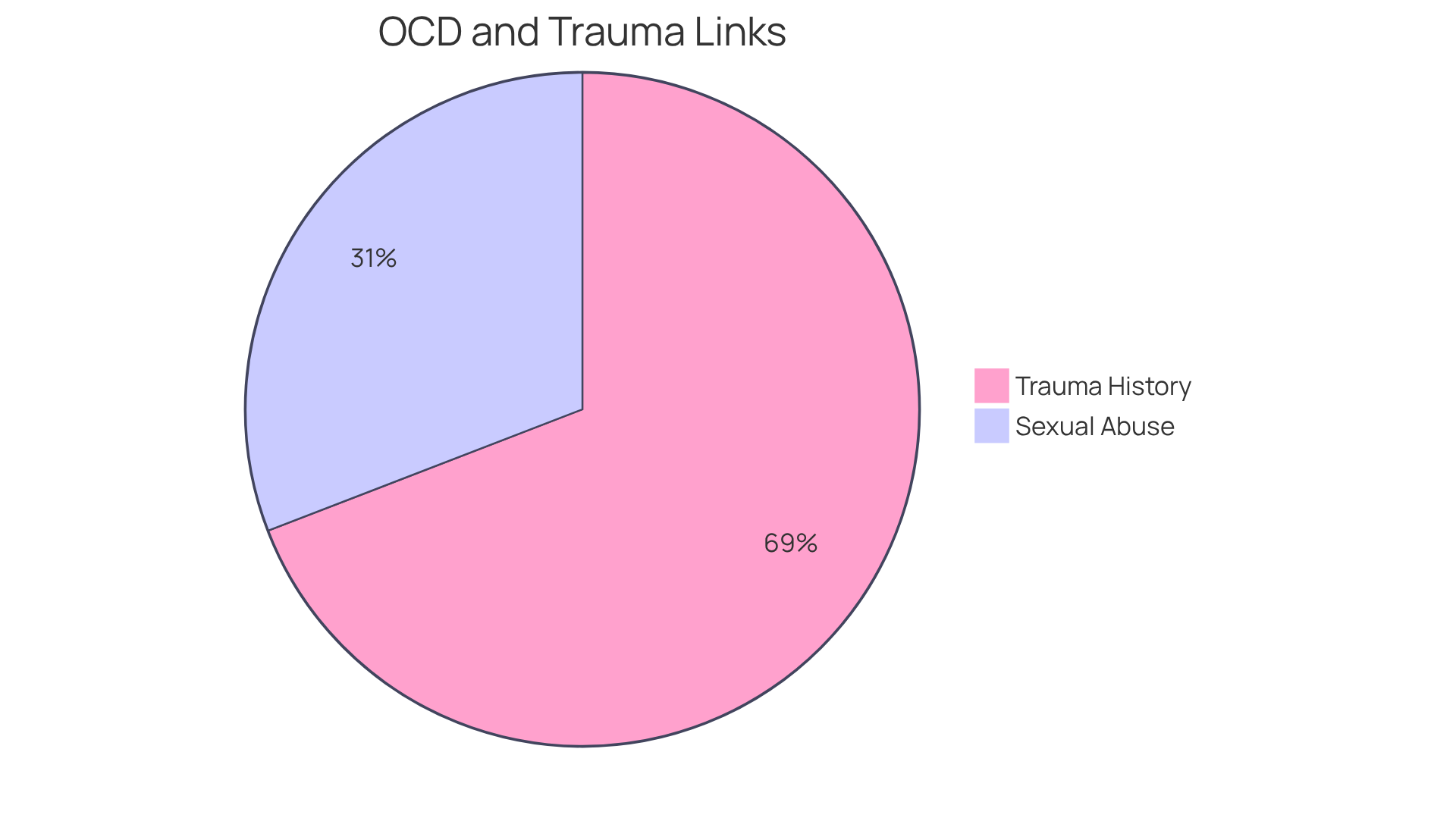
It’s important to recognize that between 30% and 82% of individuals diagnosed with OCD report having a history of trauma induced OCD. This highlights the need for integrating trauma-aware strategies into treatment plans. Recent findings reveal that certain types of distress, particularly sexual abuse, are closely associated with the emergence of trauma induced OCD symptoms. In fact, nearly 25% of survivors of such distress experience trauma induced OCD symptoms following these events.
As we explore this further, it becomes clear that mental health experts must acknowledge and address the effects of distress, especially in relation to trauma induced OCD, when developing effective therapeutic strategies. By doing so, we can foster a more compassionate approach to healing. If you or someone you know is struggling, remember that seeking help is a courageous step towards understanding and healing.
Identify Symptoms of Trauma-Induced OCD
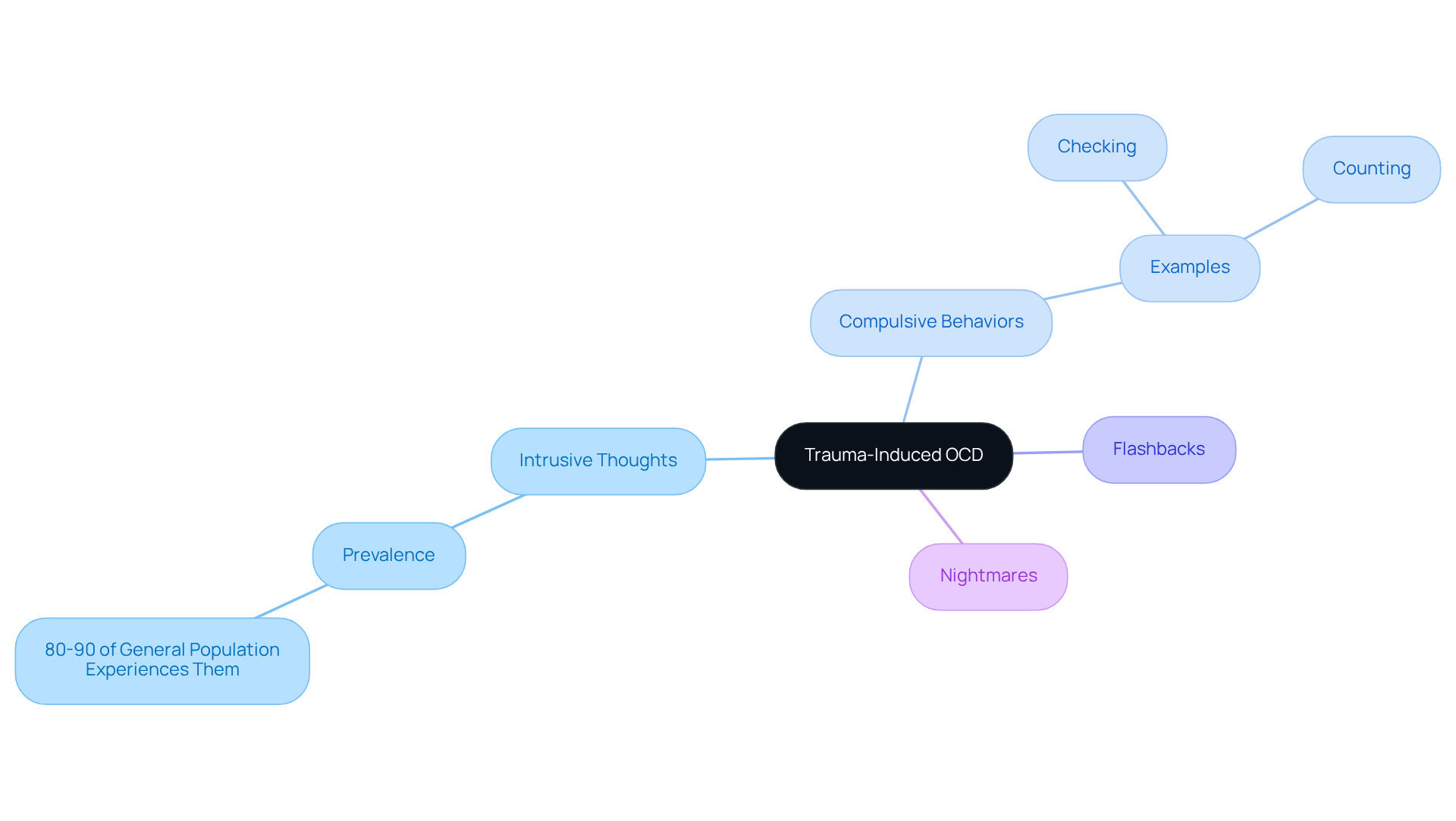
Trauma induced OCD can be incredibly challenging, often manifesting as intrusive thoughts directly linked to the traumatic experience. Alongside these thoughts, individuals may engage in compulsive behaviors, like checking or counting, all aimed at easing the anxiety that comes with these distressing memories. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? For example, someone who has gone through a traumatic car accident might find themselves obsessively checking their vehicle or counting how many times they lock the doors before they feel secure again.
In addition to these compulsions, many people report experiencing flashbacks or nightmares related to their trauma, which can intensify their OCD symptoms. It’s important to know that intrusive thoughts are quite common; research shows that 80-90% of the general population experiences them. However, only a portion of these individuals will develop OCD, often influenced by pre-existing anxiety or depression.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for starting effective treatment. Mental health experts emphasize the importance of understanding the connection between trauma and trauma induced OCD, as this knowledge can help create tailored therapeutic approaches. If you or someone you know is struggling, reaching out for support can be a vital step towards healing. Remember, you’re not alone on this journey.
Review Treatment Options for Trauma-Induced OCD
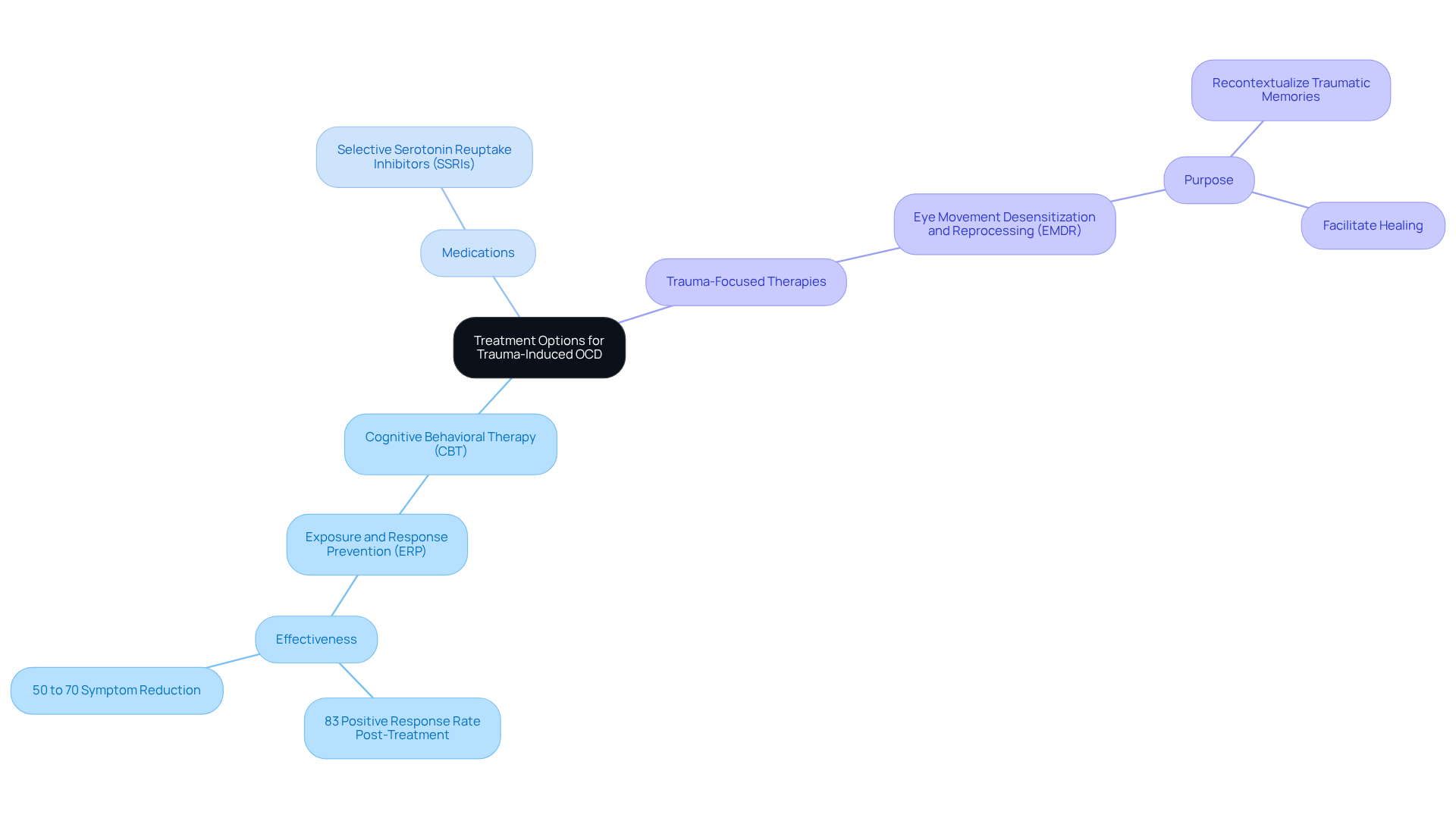
Effective treatment options for trauma induced OCD often center around Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), particularly focusing on Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP). This compassionate approach allows individuals to gently confront their fears in a supportive environment, leading to significant reductions in anxiety and compulsive behaviors. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? Studies indicate that ERP can yield a favorable response rate of up to 83% after treatment, with many clients experiencing a 50% to 70% decrease in their symptoms. Additionally, medications like Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to help manage OCD manifestations effectively.
Trauma-focused therapies, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), play a vital role in addressing the root causes of trauma induced OCD while simultaneously tackling related issues. These therapies aim to recontextualize traumatic memories, facilitating healing and symptom relief. A comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your unique needs is essential for successful recovery. It ensures that both trauma induced OCD and other trauma-related issues are addressed together, enhancing the overall effectiveness of your healing journey.
As we explore this further, remember that seeking help is a courageous step towards healing. You deserve support and understanding on this journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the deep connection between trauma and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is vital for effective treatment and support. Trauma can significantly impact mental health, and many individuals may find themselves facing trauma-induced OCD as a response to distressing events. Recognizing this relationship is essential for fostering a compassionate approach to healing and recovery.
As we explore this further, it’s important to note the prevalence of trauma-induced OCD among those with a history of trauma. This condition often comes with specific symptoms that can be challenging to navigate. Fortunately, effective therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and trauma-focused approaches, have shown promising results in alleviating symptoms and addressing the underlying trauma.
Ultimately, acknowledging the impact of trauma on OCD not only enhances our understanding but also highlights the importance of seeking help. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by your past? If so, know that you’re not alone. Those affected by trauma-induced OCD are encouraged to reach out for support, as healing is possible through tailored treatment strategies. Embracing this journey can lead to a deeper sense of well-being and resilience, reinforcing the message that no one has to face these challenges alone.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is trauma?
Trauma refers to the emotional and psychological impact resulting from distressing events such as abuse, neglect, or natural disasters, which can lead to long-lasting effects like anxiety and depression.
How does trauma relate to Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)?
Recent studies indicate that about 60% of individuals with OCD developed trauma-induced OCD after experiencing a stressful life event, demonstrating the significant impact of distress on mental health.
What are the characteristics of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)?
OCD is characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts known as obsessions, and repetitive behaviors or compulsions that individuals feel compelled to perform in response to these thoughts.
What is the prevalence of trauma-induced OCD among individuals with a traumatic background?
The prevalence of trauma-induced OCD among individuals with a traumatic background ranges from 30% to 82%, which is significantly higher compared to the general population prevalence of 1.1% to 1.8%.
Why is it important to understand the relationship between trauma and OCD?
Understanding the relationship between trauma and OCD is crucial as it highlights how distress can trigger the emergence of trauma-induced OCD, providing insight into the mental health challenges faced by individuals with traumatic experiences.
What should someone do if they are struggling with trauma or OCD?
If you or someone you know is struggling with trauma or OCD, seeking help is an important step towards healing, and it is essential to remember that you do not have to navigate this journey alone.




